设计模式 本篇的设计模式记录,主要是参考书籍 《图解设计模式》做的学习记录笔记! 回想一下,那都是多年以前的事了。最开始每个设计模式 用一片博客记录。最近,突然发现这样有点分散,想了一想,干脆直接整合到一篇博文吧。有点长,但是有目录可以快速定位到具体的设计 模式,也算方便。
Facade模式 简单窗口 使用Facade模式可以为相互关联在一起的错中复杂的类整理出高层的接口。其中的Facade角色可以让系统对外只有一个简单的接口。
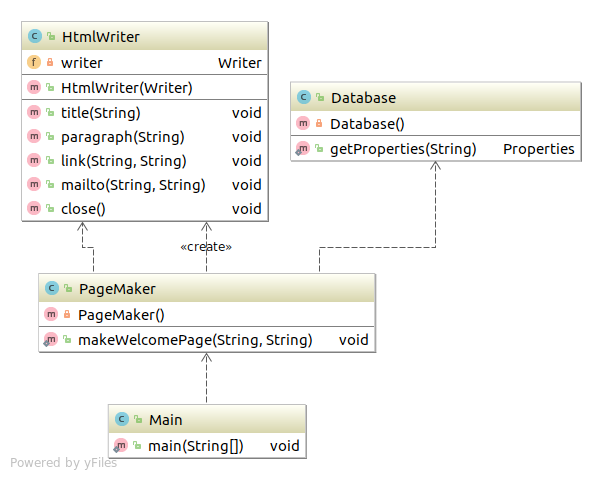
演示程序类图 Facade模式 代码 Database类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package com.sean.Facade.pagemaker;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Properties;public class Database private Database () } public static Properties getProperties (String dbname) String filename=dbname+".txt" ; Properties prop=new Properties(); try { prop.load(new FileInputStream("/home/sean/Documents/" +filename)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return prop; } }
HtmlWriter类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package com.sean.Facade.pagemaker;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.Writer;public class HtmlWriter private Writer writer; public HtmlWriter (Writer writer) this .writer=writer; } public void title (String title) try { writer.write("<html>" ); writer.write("<head>" ); writer.write("<title>" +title+"</title>" ); writer.write("</head>" ); writer.write("<body>\n" ); writer.write("<h1>" +title+"</h1>" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void paragraph (String msg) try { writer.write("<p>" +msg+"</p>" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void link (String href,String caption) paragraph("<a href=\"" +href +"\">" +caption+"</a>" ); } public void mailto (String mailaddr,String username) link("mailto:" +mailaddr,username); } public void close () try { writer.write("</body>" ); writer.write("</html>\n" ); writer.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
PageMaker类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package com.sean.Facade.pagemaker;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Properties;public class PageMaker private PageMaker () } public static void makeWelcomePage (String mailaddr,String filename) try { Properties mailprop=Database.getProperties("maildata" ); String username=mailprop.getProperty(mailaddr); HtmlWriter writer=new HtmlWriter(new FileWriter("/home/sean/Documents/" +filename)); writer.title("Welcome to " +username+"'s page!" ); writer.paragraph(username+"欢迎到来" +username+"的主页。" ); writer.paragraph("等你的邮件喔!" ); writer.mailto(mailaddr, username); writer.close(); System.out.println(filename+"is created for " +mailaddr +" (" +username+")" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Main类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package com.sean.Facade;import com.sean.Facade.pagemaker.PageMaker;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) PageMaker.makeWelcomePage("seanchristspc@gmail.com" , "welcome.html" ); } }
要点 Facade(窗口) Facade角色向系统外部提供高层接口。在实例程序中由PageMaker 扮演此角色。
构成系统的许多其他角色 这些角色各自完成自己的工作,他们并不知道Facade角色。Facade角色调用其他角色进行工作,但是其他角色不会调用Facade角色。代码中 Database 和HtmlWriter 扮演其他角色。
Client Client角色负责调用Facade角色
个人理解 Facade模式就是把复杂的系统变看起来 简单。所谓看起来简单就是指在编写代码的时候还是挺复杂的,只是在使用某个功能是对外的接口比较少而且明确。 该模式还是挺好理解的,代码也不复杂。
只有一个仲裁者 要调用多个对象之间的关系时,就需要使用Mediator模式。将控制的逻辑处理交给仲裁者。
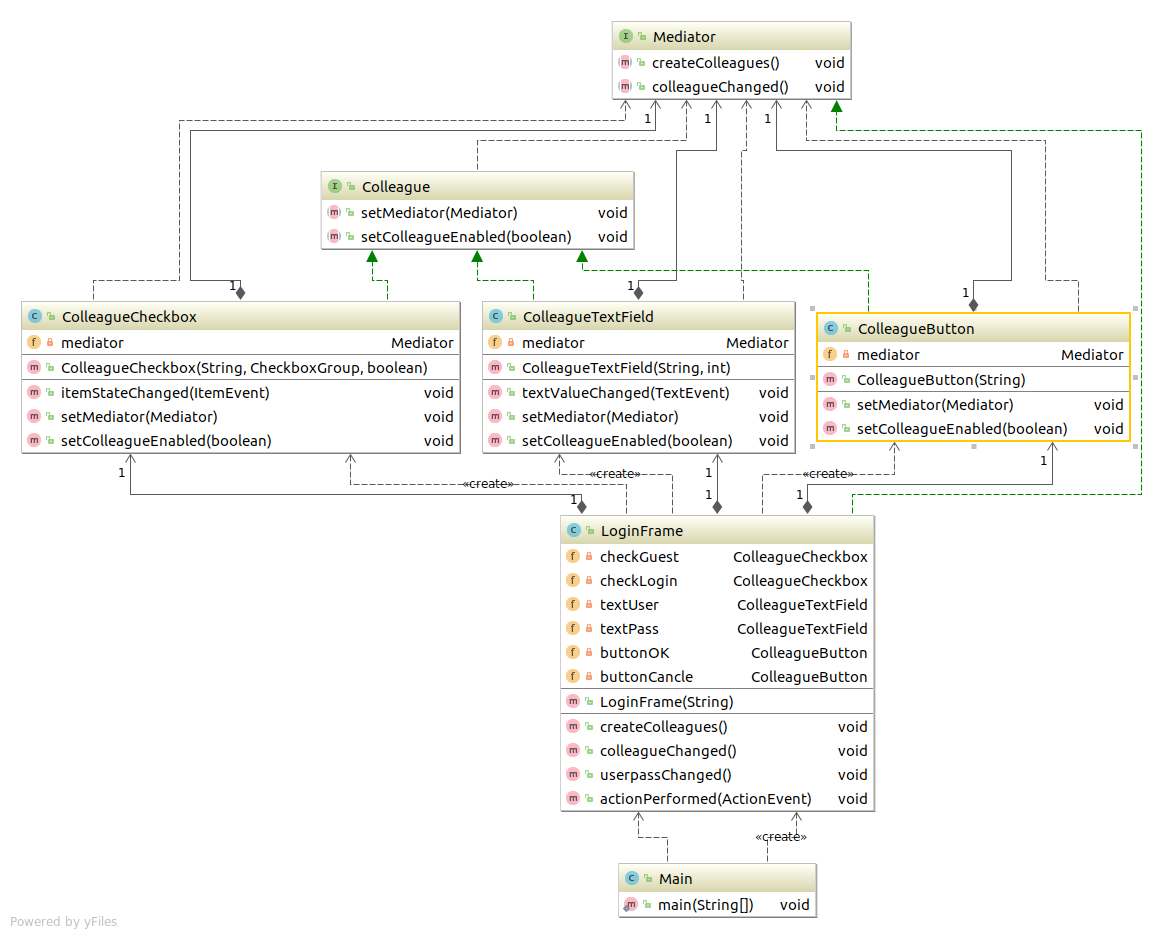
类和接口表 Mediator 定义 "仲裁者" 的接口(API)的接口 Colleague 定义"组员"的接口(API)的接口 ColleagueButton 表示按钮的类。它实现Colleague接口 ColleagueTextField 表示文本输入框的类。它实现了Colleague接口 ColleagueCheckbox 表示勾选框的类。实现了Colleague接口 LoginFrame 表示登录对话框类。实现了Mediator接口 Main 测试程序行为的类
程序的类图 有点复杂喔! 不急。慢慢看!!
代码 Colleague接口(组员接口) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.sean.Mediator;public interface Colleague public abstract void setMediator (Mediator mediator) public abstract void setColleagueEnabled (boolean enabled) }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.sean.Mediator;public interface Mediator public abstract void createColleagues () public abstract void colleagueChanged () }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import java.awt.Button;import java.awt.HeadlessException;public class ColleagueButton extends Button implements Colleague private Mediator mediator; public ColleagueButton (String caption) super (caption); } public void setMediator (Mediator mediator) this .mediator=mediator; } public void setColleagueEnabled (boolean enabled) setEnabled(enabled); } }
ColleagueCheckbox(具体的组员) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package com.sean.Mediator;import java.awt.Checkbox;import java.awt.CheckboxGroup;import java.awt.event.ItemEvent;import java.awt.event.ItemListener;public class ColleagueCheckbox extends Checkbox implements Colleague , ItemListener { private Mediator mediator; public ColleagueCheckbox (String caption,CheckboxGroup group,boolean state) super (caption,group,state); } public void itemStateChanged (ItemEvent e) mediator.colleagueChanged(); } public void setMediator (Mediator mediator) this .mediator=mediator; } public void setColleagueEnabled (boolean enabled) setEnabled(enabled); } }
ColleagueTextField(具体的组员) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.TextField;import java.awt.event.TextEvent;import java.awt.event.TextListener;public class ColleagueTextField extends TextField implements Colleague , TextListener { private Mediator mediator; public ColleagueTextField (String text,int columns) super (text,columns); } public void textValueChanged (TextEvent e) mediator.colleagueChanged(); } public void setMediator (Mediator mediator) this .mediator=mediator; } public void setColleagueEnabled (boolean enabled) setEnabled(enabled); setBackground(enabled ? Color.white : Color.lightGray); } }
LoginFrame(具体的仲裁者) 代码有点多加油看看!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 package com.sean.Mediator;import java.awt.CheckboxGroup;import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.GridLayout;import java.awt.Label;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;public class LoginFrame extends Frame implements ActionListener , Mediator private ColleagueCheckbox checkGuest; private ColleagueCheckbox checkLogin; private ColleagueTextField textUser; private ColleagueTextField textPass; private ColleagueButton buttonOK; private ColleagueButton buttonCancle; public LoginFrame (String title) super (title); setBackground(Color.lightGray); setLayout(new GridLayout(4 ,2 )); createColleagues(); add(checkGuest); add(checkLogin); add(new Label("username" )); add(textUser); add(new Label("Password" )); add(textPass); add(buttonOK); add(buttonCancle); colleagueChanged(); pack(); show(); } public void createColleagues () CheckboxGroup g= new CheckboxGroup(); checkGuest = new ColleagueCheckbox("Guest" ,g,true ); checkLogin = new ColleagueCheckbox("Login" ,g,false ); textUser = new ColleagueTextField("" ,10 ); textPass = new ColleagueTextField("" ,10 ); textPass.setEchoChar('*' ); buttonOK = new ColleagueButton("OK" ); buttonCancle = new ColleagueButton("Cancle" ); checkGuest.setMediator(this ); checkLogin.setMediator(this ); textUser.setMediator(this ); textPass.setMediator(this ); buttonOK.setMediator(this ); buttonCancle.setMediator(this ); checkGuest.addItemListener(checkGuest); checkLogin.addItemListener(checkLogin); textUser.addTextListener(textUser); textPass.addTextListener(textPass); buttonOK.addActionListener(this ); buttonCancle.addActionListener(this ); } public void colleagueChanged () if (checkGuest.getState()){ textUser.setColleagueEnabled(false ); textPass.setColleagueEnabled(false ); buttonOK.setColleagueEnabled(true ); }else { textUser.setColleagueEnabled(true ); userpassChanged(); } } public void userpassChanged () if (textUser.getText().length()>0 ){ textPass.setColleagueEnabled(true ); if (textPass.getText().length()>0 ){ buttonOK.setColleagueEnabled(true ); }else { buttonOK.setColleagueEnabled(false ); } }else { textPass.setColleagueEnabled(false ); buttonOK.setColleagueEnabled(false ); } } public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e) System.out.println(e.toString()); System.exit(0 ); } }
主函数 调用者 客户 代码比较少!放松!放松!放松!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package com.sean.Mediator;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) LoginFrame lf=new LoginFrame("Mediator Sample" ); } }
个人理解 Mediator模式就如同在一个集体中需要一个管理者,没管理者就是一团乱麻!有管理者,能让程序有序的进行!虽然我们崇尚自由!但是没有管理的世界更可怕!生活中需要管理者,程序中也需要管理者!程序来源于生活。
Command模式 命令也是类
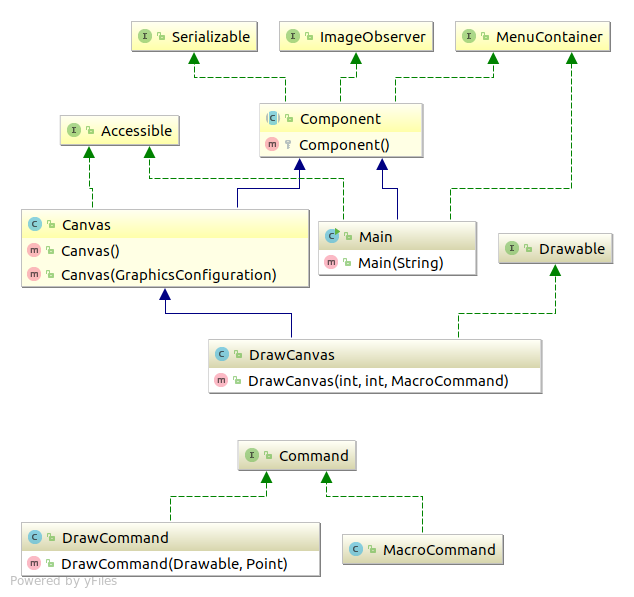
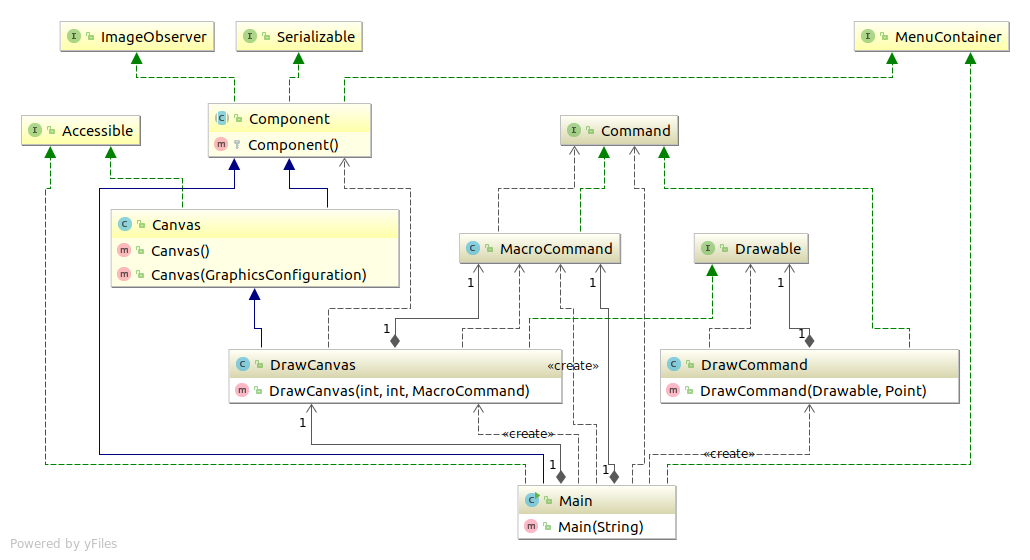
类表 command Command 表示命令 的接口 command MacroCommand 表示 由多条命令整合成的命令 的类 drawer DrawCommand 表示 绘制一个点的命令 的类 drawer Drawable 表示 绘制对象 的接口 drawer DrawCanvas 实现 绘制对象 的类 无名 Main 测试程序行为的类
类图 粗略一点的
详细一点
code Command 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 package com.sean.Command.command;public interface Command public abstract void execute () }
MacroCommand 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package com.sean.Command.command;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Stack;public class MacroCommand implements Command private Stack commands = new Stack(); public void execute () Iterator it=commands.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ ((Command)it.next()).execute(); } } public void append (Command command) if (command != this ){ commands.push(command); } } public void undo () if (!commands.empty()){ commands.pop(); } } public void clear () commands.clear(); } }
Drawable 1 2 3 4 5 6 package com.sean.Command.drawer;public interface Drawable public abstract void draw (int x,int y) }
DrawCanvas 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package com.sean.Command.drawer;import java.awt.Canvas;import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.Graphics;import com.sean.Command.command.MacroCommand;public class DrawCanvas extends Canvas implements Drawable private Color color =Color.red; private int radius=6 ; private MacroCommand history; public DrawCanvas (int width,int height,MacroCommand history) setSize(width, height); setBackground(Color.WHITE); this .history=history; } public void paint (Graphics g) history.execute(); } public void draw (int x, int y) Graphics g=getGraphics(); g.setColor(color); g.fillOval(x-radius, y-radius, radius*2 , radius*2 ); } }
DrawCommand 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package com.sean.Command.drawer;import java.awt.Point;import com.sean.Command.command.Command;public class DrawCommand implements Command protected Drawable drawable; private Point position; public DrawCommand (Drawable drawable,Point position ) this .drawable=drawable; this .position=position; } public void execute () drawable.draw(position.x, position.y); } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 package com.sean.Command;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;import java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;import java.awt.event.WindowListener;import javax.swing.Box;import javax.swing.BoxLayout;import javax.swing.JButton;import javax.swing.JFrame;import com.sean.Command.command.Command;import com.sean.Command.command.MacroCommand;import com.sean.Command.drawer.DrawCanvas;import com.sean.Command.drawer.DrawCommand;public class Main extends JFrame implements ActionListener , MouseMotionListener , WindowListener { private MacroCommand history=new MacroCommand(); private DrawCanvas canvas=new DrawCanvas(400 ,400 ,history); private JButton clearButton=new JButton("clear" ); public Main (String title) super (title); this .addWindowListener(this ); canvas.addMouseMotionListener(this ); clearButton.addActionListener(this ); Box buttonBox=new Box(BoxLayout.X_AXIS); buttonBox.add(clearButton); Box mainBox=new Box(BoxLayout.Y_AXIS); mainBox.add(buttonBox); mainBox.add(canvas); getContentPane().add(mainBox); pack(); show(); } public void windowOpened (WindowEvent e) } public void windowClosing (WindowEvent e) System.exit(0 ); } public void windowClosed (WindowEvent e) } public void windowIconified (WindowEvent e) } public void windowDeiconified (WindowEvent e) } public void windowActivated (WindowEvent e) } public void windowDeactivated (WindowEvent e) } public void mouseDragged (MouseEvent e) Command command=new DrawCommand(canvas,e.getPoint()); history.append(command); command.execute(); } public void mouseMoved (MouseEvent e) } public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e) if (e.getSource()==clearButton){ history.clear(); canvas.repaint(); } } public static void main (String[] args) new Main("Command Pattern" ); } }
State模式 用类表示状态
类图 有点复杂!但只有部分是自己写的,其他是java类库内的类。
State 粗略简单一点的类图
代码 State 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.sean.State;public interface State public abstract void doClock (Context context,int hour) public abstract void doUse (Context context) public abstract void doAlarm (Context context) public abstract void doPhone (Context context) }
NightState(具体的状态) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 package com.sean.State;public class NightState implements State private static NightState singleton = new NightState(); private NightState () } public static State getInstance () return singleton; } public void doClock (Context context, int hour) if (9 <=hour || hour<17 ){ context.changeState(DayState.getInstance()); } } public void doUse (Context context) context.callSecurityCenter("紧急!晚上使用金库!" ); } public void doAlarm (Context context) context.callSecurityCenter("按下警铃(晚上)" ); } public void doPhone (Context context) context.callSecurityCenter("晚上通话录音" ); } public String toString () return "[晚上]" ; } }
DayState(具体的状态) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 package com.sean.State;public class DayState implements State private static DayState singleton = new DayState(); private DayState () } public static State getInstance () return singleton; } public void doClock (Context context, int hour) if (hour<9 || 17 <=hour){ context.changeState(NightState.getInstance()); } } public void doUse (Context context) context.recordLog("使用金库(白天)" ); } public void doAlarm (Context context) context.callSecurityCenter("按下警铃(白天)" ); } public void doPhone (Context context) context.callSecurityCenter("正常通话(白天)" ); } public String toString () return "[白天]" ; } }
Context 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.sean.State;public interface Context public abstract void setClock (int hour) public abstract State changeState (State state) public abstract void callSecurityCenter (String msg) public abstract void recordLog (String msg) }
SafeFrame 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 package com.sean.State;import java.awt.BorderLayout;import java.awt.Button;import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.Panel;import java.awt.TextArea;import java.awt.TextField;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;public class SafeFrame extends Frame implements ActionListener , Context private TextField textClock = new TextField(60 ); private TextArea textScreen=new TextArea(10 ,60 ); private Button buttonUse=new Button("使用金库" ); private Button buttonAlarm=new Button("按下警铃" ); private Button buttonPhone=new Button("正常通话" ); private Button buttonExit=new Button("结束" ); private State state=DayState.getInstance(); public SafeFrame (String title) super (title); setBackground(Color.lightGray); setLayout(new BorderLayout()); add(textClock,BorderLayout.NORTH); textClock.setEditable(false ); add(textScreen,BorderLayout.CENTER); textScreen.setEditable(false ); Panel panel=new Panel(); panel.add(buttonUse); panel.add(buttonAlarm); panel.add(buttonPhone); panel.add(buttonExit); add(panel,BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); show(); buttonUse.addActionListener(this ); buttonAlarm.addActionListener(this ); buttonPhone.addActionListener(this ); buttonExit.addActionListener(this ); } public void setClock (int hour) String clockstring="现在时间是:" ; if (hour<10 ){ clockstring+="0" +hour+":00" ; }else { clockstring+=hour+":00" ; } System.out.println(clockstring); textClock.setText(clockstring); state.doClock(this , hour); } public State changeState (State state) System.out.println("从" +this .state+"状态变为了" +state+"状态" ); this .state=state; return state; } public void callSecurityCenter (String msg) textScreen.append("Call!" +msg+"\n" ); } public void recordLog (String msg) textScreen.append("record ... " +msg+"\n" ); } public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e) System.out.println(e.toString()); if (e.getSource()==buttonUse){ state.doUse(this ); }else if (e.getSource()==buttonAlarm) { state.doAlarm(this ); }else if (e.getSource()==buttonPhone) { state.doPhone(this ); }else if (e.getSource()== buttonExit) { System.exit(0 ); }else { System.out.println("?" ); } } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package com.sean.State;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) SafeFrame frame=new SafeFrame("state module" ); while (true ){ for (int hour=0 ;hour<24 ;hour++){ frame.setClock(hour); try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
要点 采用分而治之方针。 定义接口,声明抽象方法 定义多个类,实现具体的方法
Memento模式 保存对象状态 ### 类表 | 名字 | 说明 | |--------|--------| | Memento | 表示Gamer状态的类 | | Gamer | 表示游戏主人公的类,他会生成Memento实例 | | Main | 进行游戏的类。他会事先保存Memento的实例,之后会根据需要回复Gamer的状态 |
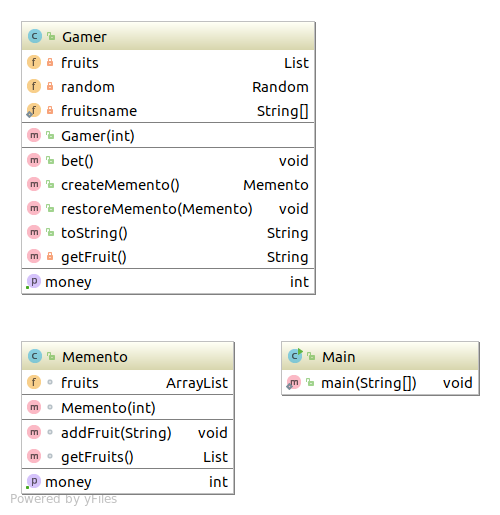
类图 Memento 代码 Memento类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import com.sean.AbstractFactory.listfactory.ListLink;public class Memento int money; ArrayList fruits; public int getMoney () return money; } Memento(int money){ this .money=money; this .fruits=new ArrayList(); } void addFruit (String fruit) fruits.add(fruit); } List getFruits () { return (List) fruits.clone(); } }
Gamer类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 package com.sean.Memento;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.List;import java.util.Random;public class Gamer private int money; private List fruits=new ArrayList(); private Random random=new Random(); private static String[] fruitsname={"苹果" ,"葡萄" ,"香蕉" ,"橘子" }; public Gamer (int money) this .money=money; } public int getMoney () return money; } public void bet () int dice = random.nextInt(6 )+1 ; if (dice==1 ){ money+=100 ; System.out.println("所持金币增加了。" ); }else if (dice==2 ) { money/=2 ; System.out.println("所持金币减半。" ); }else if (dice==6 ) { String f=getFruit(); System.out.println("获得的水果" +f+")。" ); }else { System.out.println("什么都没发生。" ); } } public Memento createMemento () Memento m=new Memento(money); Iterator it=fruits.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ String f=(String)it.next(); if (f.startsWith("好吃的" )){ m.addFruit(f); } } return m; } public void restoreMemento (Memento memento) this .money=money; this .fruits=memento.getFruits(); } public String toString () return "[money= " +money+",fruits= " +fruits+"]" ; } private String getFruit () String prefix="" ; if (random.nextBoolean()){ prefix="好吃的" ; } return prefix+fruitsname[random.nextInt(fruitsname.length)]; } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package com.sean.Memento;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) Gamer gamer=new Gamer(100 ); Memento memento=gamer.createMemento(); for (int i=0 ;i<100 ;i++){ System.out.println("========" +i); System.out.println("当前状态:" +gamer); gamer.bet(); System.out.println("所持金钱为" +gamer.getMoney()+"元" ); if (gamer.getMoney()>memento.getMoney()){ System.out.println("(所持金钱增加许多,因此保存游戏当前状态)" ); memento=gamer.createMemento(); }else if (gamer.getMoney()<memento.getMoney()/2 ) { System.out.println("(所持金钱减少许多,因此要恢复至以前状态)" ); gamer.restoreMemento(memento); } try { Thread.sleep(100 ); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("" ); } } }
个人理解 Memento模式就是实现对象状态的恢复,而设置的。
Observe模式 在Observe模式中,当观察对象的状态发生变化,会通知给观察者。Observe模式适用于根据对象状态进行相应的处理场景。
类和接口的表 Observer 表示观察者接口 NumberGenerator 表示生成数值的对象的抽象类 RandomNumberGenerator 生成随机数的类 DigitObserver 表示以数字形式显示数值类 GraphObserver 表示以简单的图形显示数值类 Main 测试程序行为的类
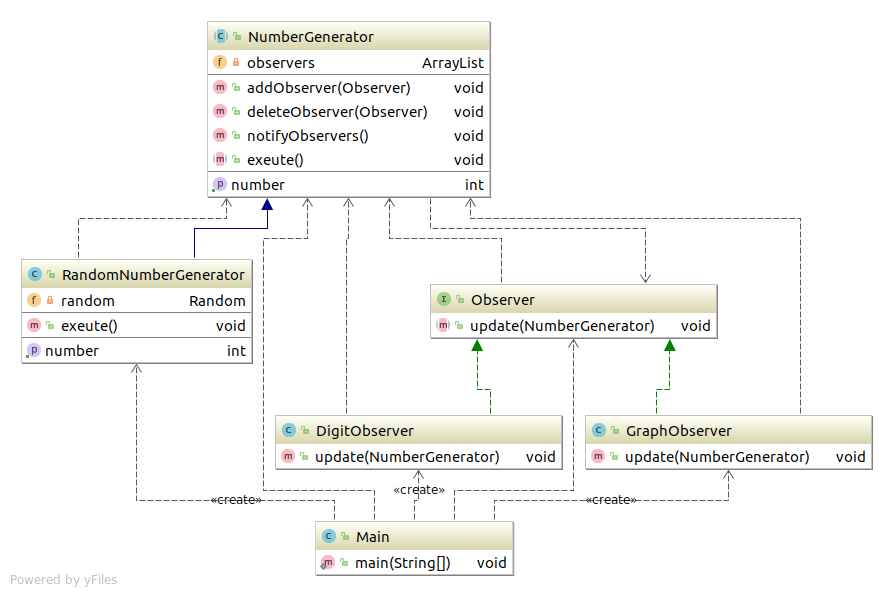
程序类图 Observer 代码 Observer接口(定义抽象方法) 1 2 3 4 5 package com.sean.Observer;public interface Observer public abstract void update (NumberGenerator generator) }
NumberGenerator抽象类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package com.sean.Observer;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Iterator;public abstract class NumberGenerator private ArrayList observers = new ArrayList(); public void addObserver (Observer observer) observers.add(observer); } public void deleteObserver (Observer observer) observers.remove(observer); } public void notifyObservers () Iterator it=observers.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ Observer o=(Observer) it.next(); o.update(this ); } } public abstract int getNumber () public abstract void exeute () }
DigitObserver具体的观察者 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package com.sean.Observer;public class DigitObserver implements Observer public void update (NumberGenerator generator) System.out.println("DigitObserver:" +generator.getNumber()); try { Thread.sleep(100 ); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
GraphObserver具体的观察者 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package com.sean.Observer;public class GraphObserver implements Observer public void update (NumberGenerator generator) System.out.println("GraphObserver:" ); int count = generator.getNumber(); for (int i=0 ;i<count;i++){ System.out.print("*" ); } System.out.println("" ); try { Thread.sleep(100 ); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
RandomNumberGenerator具体的被观察对象 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package com.sean.Observer;import java.util.Random;public class RandomNumberGenerator extends NumberGenerator private Random random= new Random(); private int number; @Override public int getNumber () return number; } @Override public void exeute () for (int i=0 ;i<20 ;i++){ number=random.nextInt(50 ); notifyObservers(); } } }
测试方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 ackage com.sean.Observer; public class Main public static void main (String[] args) NumberGenerator generator=new RandomNumberGenerator(); Observer observer1=new DigitObserver(); Observer observer2=new GraphObserver(); generator.addObserver(observer1); generator.addObserver(observer2); generator.exeute(); } }
要点 Observer角色并非主动去观察,而是被动去观察,被动的接受观察对象的通知。
Flyweight 模式 共享 对象,避免浪费。
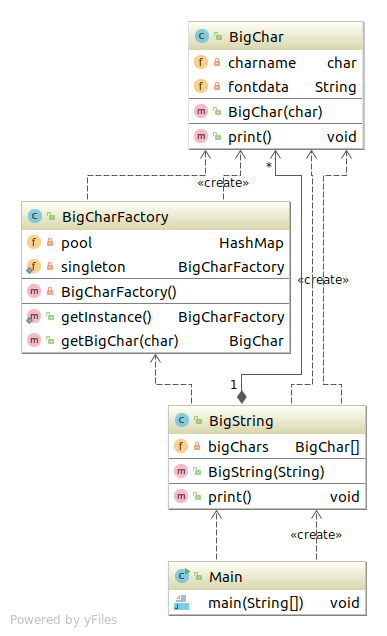
类表 BigChar 表示"大型字符"类 BigCharFactory 表示生成和共用BigChar类的实例的类 BigString 表示多个BigChar组成的 "大型字符串" 的类 Main 测试程序行为的类
程序类图 Flyweight 代码 BigChar类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.IOException;public class BigChar private char charname; private String fontdata; public BigChar (char charname) this .charname=charname; try { BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("/home/sean/Documents/" +"big" +charname+".txt" )); String line; StringBuffer buf=new StringBuffer(); while ((line=reader.readLine())!=null ){ buf.append(line); buf.append("\n" ); } reader.close(); this .fontdata=buf.toString(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { this .fontdata=charname+"?" ; e.printStackTrace(); } } public void print () System.out.print(fontdata); } }
BigCharFactory类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package com.sean.Flyweight;import java.util.HashMap;public class BigCharFactory private HashMap pool=new HashMap(); private static BigCharFactory singleton=new BigCharFactory(); private BigCharFactory () } public static BigCharFactory getInstance () return singleton; } public synchronized BigChar getBigChar (char charname) BigChar bc=(BigChar) pool.get("" +charname); if (bc==null ){ bc=new BigChar(charname); pool.put("" +charname, bc); } return bc; } }
BigString类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 package com.sean.Flyweight;public class BigString private BigChar[] bigChars; public BigString (String string) bigChars=new BigChar[string.length()]; BigCharFactory factory=BigCharFactory.getInstance(); for (int i=0 ;i<bigChars.length;i++){ bigChars[i]=factory.getBigChar(string.charAt(i)); } } public void print () for (int i=0 ;i<bigChars.length;i++){ bigChars[i].print(); } } }
Main类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package com.sean.Flyweight;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) BigString bs=new BigString("10101" ); bs.print(); } }
要点 Flyweight模式会对多个地方产生影响 。
Intrinsic: 应当被共享的信息Extrinsic: 不应当被共享的信息
Instrinsic信息 不依赖位置状况,可以共享 Extrinsic信息 依赖位置与状况,不能共享
不要让被共享的实例被垃圾回收机器回收 Flyweight优点:共享实例能减少对内存的使用,并且能提高运行的速度。
Adapter模式 加个 "适配器" 以便复用 Adapter模式也被称为Wrapper(包装器)模式。
Adapter模式 类适配器模式(使用继承的适配器) 对象适配器模式(使用委托的适配器)
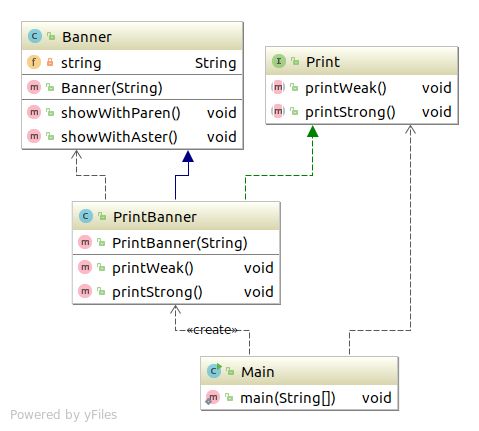
类适配器模式(使用继承的适配器) 类图 Adapter Design Pattern code Print 1 2 3 4 5 6 package com.sean.Adapter.a;public interface Print public abstract void printWeak () public abstract void printStrong () }
Banner 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package com.sean.Adapter.a;public class Banner private String string; public Banner (String string) this .string=string; } public void showWithParen () System.out.println("(" +string+")" ); } public void showWithAster () System.out.println("*" +string+"*" ); } }
PrintBanner 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package com.sean.Adapter.a;public class PrintBanner extends Banner implements Print public PrintBanner (String string) super (string); } public void printWeak () showWithParen(); } public void printStrong () showWithAster(); } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.sean.Adapter.a;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) Print print = new PrintBanner("Hello" ); print.printWeak(); print.printStrong(); } }
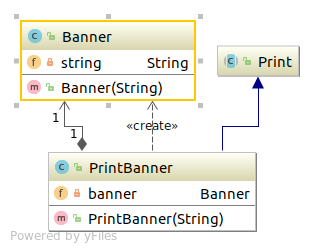
对象适配器模式(使用委托的适配器) 类图 Adapter Design Pattern proxy code Banner 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package com.sean.Adapter.b;public class Banner private String string; public Banner (String string) this .string=string; } public void showWithParen () System.out.println("(" +string+")" ); } public void showWithAster () System.out.println("*" +string+"*" ); } }
Print 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 package com.sean.Adapter.b;public abstract class Print public abstract void printWeak () public abstract void printStrong () }
PrintBanner 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package com.sean.Adapter.b;public class PrintBanner extends Print private Banner banner; public PrintBanner (String string) this .banner = new Banner(string); } @Override public void printWeak () banner.showWithParen(); } @Override public void printStrong () banner.showWithAster(); } }
要点 Adapter模式会对现有的类进行适配,生成行的类。 版本的升级与兼容需要用到Adapter模式。 适配!适配!就是给需要的类配对一个合适的插口。
FactoryMethod模式 将实例的生成交给子类用TemplateMethod模式来构建 生成的实例的工厂 , 就是FactoryMethod模式。
类图 Factory code Factory 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.sean.FactoryMethod.framework;public abstract class Factory public final Product create (String owner) Product product=createProduct(owner); registerProduct(product); return product; } protected abstract Product createProduct (String owner) protected abstract void registerProduct (Product product) }
Product 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 package com.sean.FactoryMethod.framework;public abstract class Product public abstract void use () }
IDCard 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 package com.sean.FactoryMethod.idcard;import com.sean.FactoryMethod.framework.Product;public class IDCard extends Product private String owner; IDCard(String owner){ System.out.println("制作" +owner+"的ID卡。" ); this .owner=owner; } @Override public void use () System.out.println("使用" +owner+"的ID卡。" ); } public String getOwner () return owner; } }
IDCardFactory 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package com.sean.FactoryMethod.idcard;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import com.sean.FactoryMethod.framework.Factory;import com.sean.FactoryMethod.framework.Product;public class IDCardFactory extends Factory private List owners = new ArrayList(); @Override protected Product createProduct (String owner) return new IDCard(owner); } @Override protected void registerProduct (Product product) owners.add(((IDCard)product).getOwner()); } public List getOwners () return owners; } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package com.sean.FactoryMethod;import com.sean.FactoryMethod.framework.Factory;import com.sean.FactoryMethod.framework.Product;import com.sean.FactoryMethod.idcard.IDCardFactory;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) Factory factory=new IDCardFactory(); Product card1= factory.create("小明" ); Product card2=factory.create("小红" ); Product card3=factory.create("小刚" ); card1.use(); card2.use(); card3.use(); } }
要点 工厂产生产品 具体的工厂产生具体的产品 这两者形成一一对应的关系。
TemplateMethod模式 将具体处理交给子类 带有模板功能的模式。 在父类中定义处理流程的框架,在子类中实现具体处理的模式就称为TemplateMethod模式。 在抽象类阶段确定处理的流程非常重要。
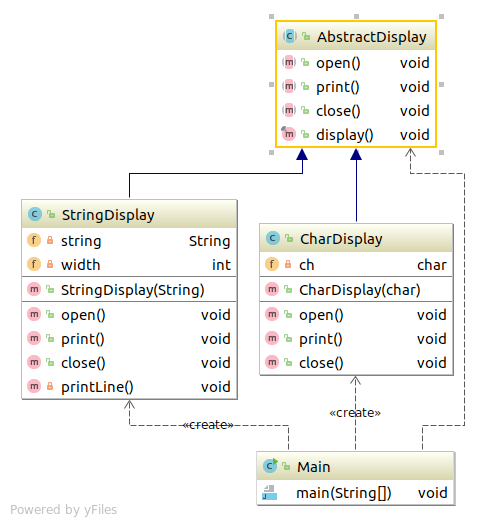
类图 TemplateMethod 代码 AbstractDisplay 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package com.sean.TemplateMethod;public abstract class AbstractDisplay public abstract void open () public abstract void print () public abstract void close () public final void display () open(); for (int i=0 ;i<5 ;i++){ print(); } close(); } }
CharDisplay 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package com.sean.TemplateMethod;public class CharDisplay extends AbstractDisplay private char ch; public CharDisplay (char ch) this .ch=ch; } @Override public void open () System.out.print("<<" ); } @Override public void print () System.out.print(ch); } @Override public void close () System.out.println(">>" ); } }
StringDisplay 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package com.sean.TemplateMethod;public class StringDisplay extends AbstractDisplay private String string; private int width; public StringDisplay (String string) this .string=string; this .width=string.getBytes().length; } @Override public void open () printLine(); } @Override public void print () System.out.println("|" +string+"|" ); } @Override public void close () printLine(); } private void printLine () System.out.print("+" ); for (int i=0 ;i<width;i++){ System.out.print("-" ); } System.out.println("+" ); } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package com.sean.TemplateMethod;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) AbstractDisplay d1=new CharDisplay('H' ); AbstractDisplay d2=new StringDisplay("Hello,world" ); d1.display(); d2.display(); } }
要点 Template Method模式中,父类与子类是紧密联系,共同工作的。在子类中实现父类的抽象方法。
Proxy模式 只在必要时生成实例
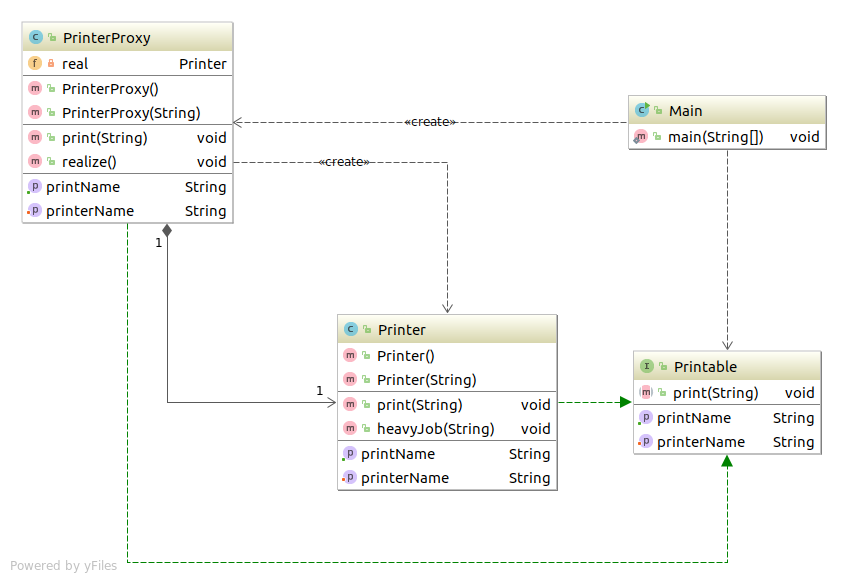
类表 Printer 表示带名字的打印机类(本人) Printable Printer和PrinterProxy的共同接口 PrinterProxy 表示带名字的打印机类(代理人) Main 测试程序行为的类
类图 Proxy 代码 Printable接口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package com.sean.Proxy;public interface Printable public abstract void setPrinterName (String name) public abstract String getPrintName () public abstract void print (String string) }
Printer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.sean.Proxy;public class Printer implements Printable private String name; public Printer () } public Printer (String name) this .name=name; heavyJob("正在生成Printer实例(" +name+")" ); } public void setPrinterName (String name) this .name=name; } public String getPrintName () return name; } public void print (String string) System.out.println("====" +name+"====" ); System.out.println(string); } public void heavyJob (String msg) System.out.print(msg); for (int i=0 ;i<5 ;i++){ try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.print("." ); } System.out.println("结束。" ); } }
PrinterProxy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package com.sean.Proxy;public class PrinterProxy implements Printable private String name; private Printer real; public PrinterProxy () } public PrinterProxy (String name) this .name=name; } public synchronized void setPrinterName (String name) if (real!=null ){ real.setPrinterName(name); } this .name=name; } public String getPrintName () return name; } public void print (String string) realize(); real.print(string); } public synchronized void realize () if (real==null ){ real=new Printer(name); } } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package com.sean.Proxy;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) Printable p=new PrinterProxy("Alice" ); System.out.println("现在的名字是" +p.getPrintName()+"。" ); p.setPrinterName("Bob" ); System.out.println("现在的名字是" +p.getPrintName()+"。" ); p.print("Hello,world!" ); } }
Iterator模式 一个一个遍历 迭代器
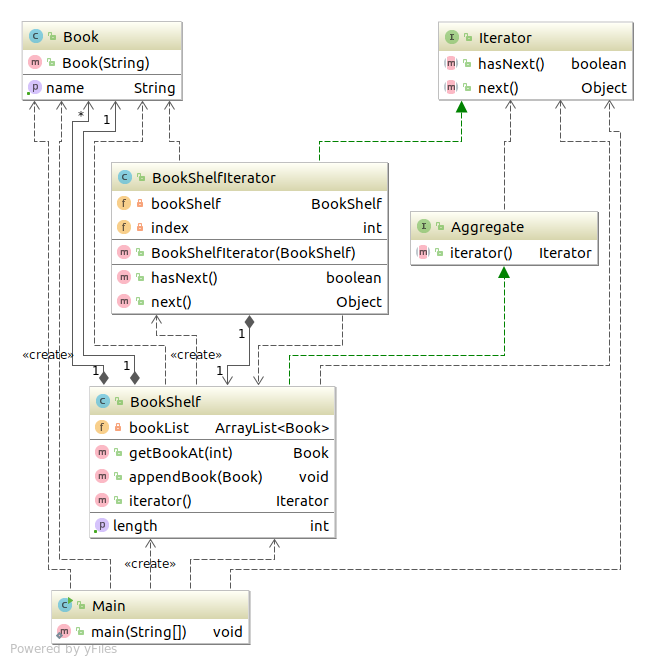
类图 Iterator code Aggregate 1 2 3 4 5 package com.sean.Iterator;public interface Aggregate public abstract Iterator iterator () }
Iterator 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 package com.sean.Iterator;public interface Iterator public abstract boolean hasNext () public abstract Object next () }
Book 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.sean.Iterator;public class Book private String name; public Book (String name) this .name=name; } public String getName () return name; } }
BookShelf 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package com.sean.Iterator;import java.util.ArrayList;public class BookShelf implements Aggregate private ArrayList<Book> bookList = new ArrayList<Book>(); private int last=0 ; public Book getBookAt (int index) { return bookList.get(index); } public void appendBook (Book book) bookList.add(book); last++; } public int getLength () return last; } public Iterator iterator () return new BookShelfIterator(this ); } }
BookShelfIterator 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package com.sean.Iterator;public class BookShelfIterator implements Iterator private BookShelf bookShelf; private int index; public BookShelfIterator (BookShelf bookShelf) this .bookShelf = bookShelf; this .index=0 ; } public boolean hasNext () if (index < bookShelf.getLength()){ return true ; }else { return false ; } } public Object next () Book book = bookShelf.getBookAt(index); index++; return book; } }
Main 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package com.sean.Iterator;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Around the World in 80 Days" )); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Bible" )); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Cinderella" )); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Dady-Long-Legs" )); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Gone with the wind!" )); Iterator it = bookShelf.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ Book book = (Book) it.next(); System.out.println(book.getName()); } } }
参照 《图解设计模式》
写这个只是为了加深自己对设计模式的理解,如不明白,可以看 《图解设计模式》。 程序类图使用idea 生成的
备注 I would greatly appreciate hearing about any error in this article, even minor ones. I welcome your suggestions for improvements, even tiny one. Please email to me! 😤